Blockchain¶
In this section we will take a brief look at the Blockchain component of asvin architecture and explain it briefly.
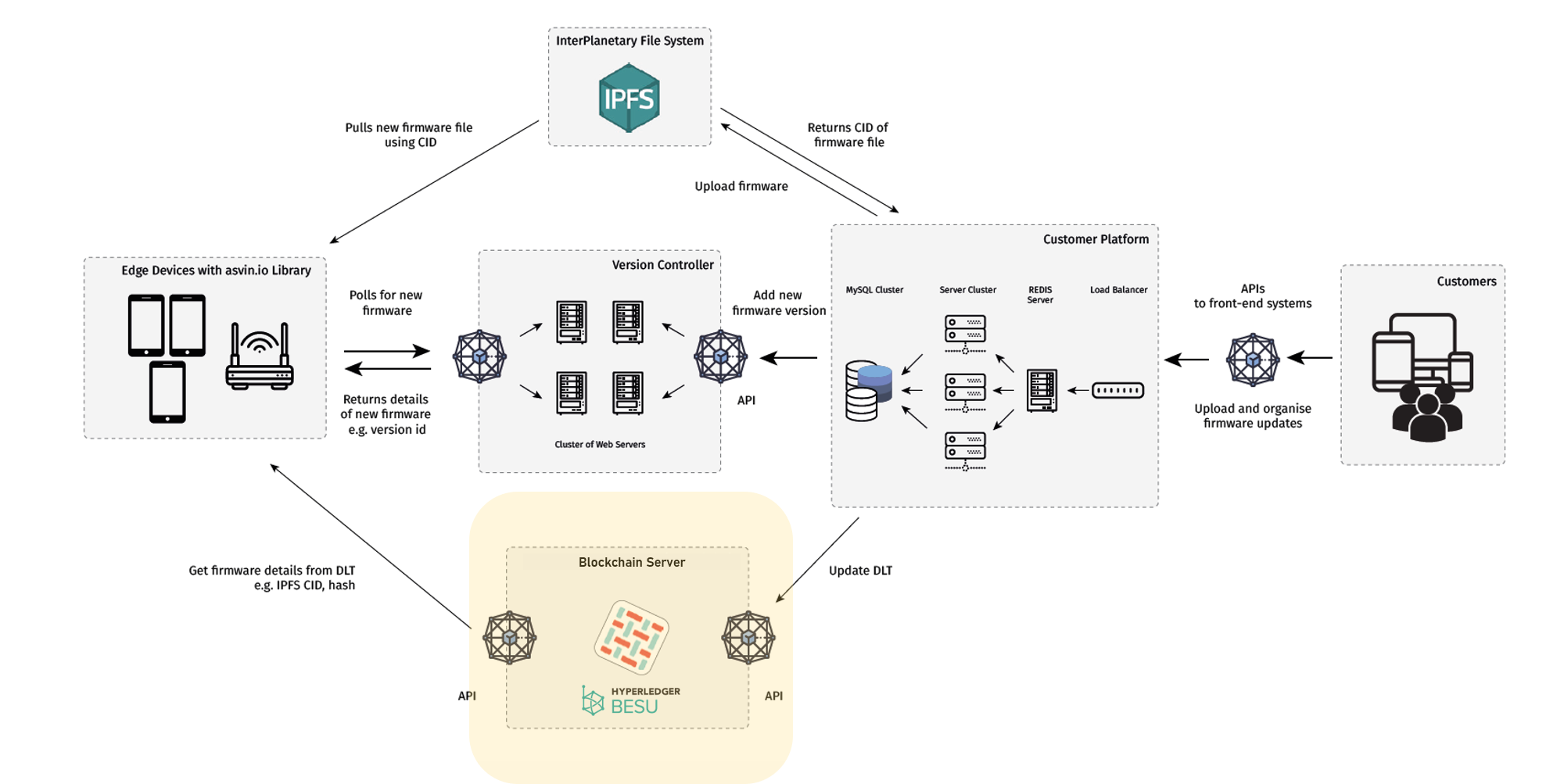
Blockchain is a type of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) which contains a growing list of records known as blocks. Each block contains the cryptographic hash of the previous block. By design, blockchains are resistant to modification of the data stored on them.
In the asvin architecture, we have built the blockchain network based on Hyperledger Fabric and Hyperledger besu. Customers can choose to use either of the two blockchains for their deployments. These blockchain networks provide a ledger that stores all transactions executed on the asvin.io network, e.g: device register, firmware upload, device update, firmware update, and user registration. Each of these transactions are paired with unique hashes and are stored in blocks which are again linked with a secured hash. This process provides security and immutability to the ledger. The asvin.io platform is designed for unlimited scalability with a cluster of servers which runs Fabric & Besu networks to administer the requirements to maintain functionality to millions of IoT devices.
Hyperledger Fabric¶
The pluggable modules of the Fabric network allow maximum flexibility to asvin.io infrastructure, enabling asvin.io to develop bespoke solutions for its IoT customers. The cluster is developed using Docker swarm.
The fabric has following modules and services:
Peer: an entity in the Fabric network which receives request from applications, runs a chaincode, validates transactions and maintains ledger.
Orderer: This service orders all the transactions happening in the Fabric network and forward them to peers to be validated
MSP: provides digital identities to every member of the Fabric network.
Storage: Fabric network uses CouchDB to store the current state of ledger data.
Hyperledger Besu¶
Hyperledger Besu is an open source Ethereum client. It can be run on the Ethereum public network or on private permissioned networks.
Hyperledger Besu’s features include:
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the Turing complete virtual machine that allows the deployment and execution of smart contracts via transactions within an Ethereum blockchain.
Consensus Algorithms are involved in transaction validation, block validation, and block production (i.e., mining in Proof of Work).
RocksDB key-value database to persist chain data locally is used for storage.
P2P networking via Ethereum’s devp2p network protocols for inter-client communication and an additional sub-protocol for IBFT2.
User-facing mainnet Ethereum and EEA JSON-RPC APIs over HTTP and WebSocket protocols as well as a GraphQL API.
Node performance is monitored using Prometheus or the debug_metrics JSON-RPC API method. Network Performance is monitored with Alethio tools such as Block Explorer and EthStats Network Monitor.
Privacy in Hyperledger Besu refers to the ability to keep transactions private between the involved parties. Other parties cannot access the transaction content, sending party, or list of participating parties. Besu uses a Private Transaction Manager to implement privacy.
A permissioned network allows only specified nodes and accounts to participate by enabling node permissioning and/or account permissioning on the network.
The operating system level virtualization is achieved on blockchain server using docker. Each service in the network runs in a separate docker container and these containers are hosted on multiple machines on the cluster. The communication among containers is achieved using docker swarm. The whole blockchain network is developed and run using docker swarm technology.