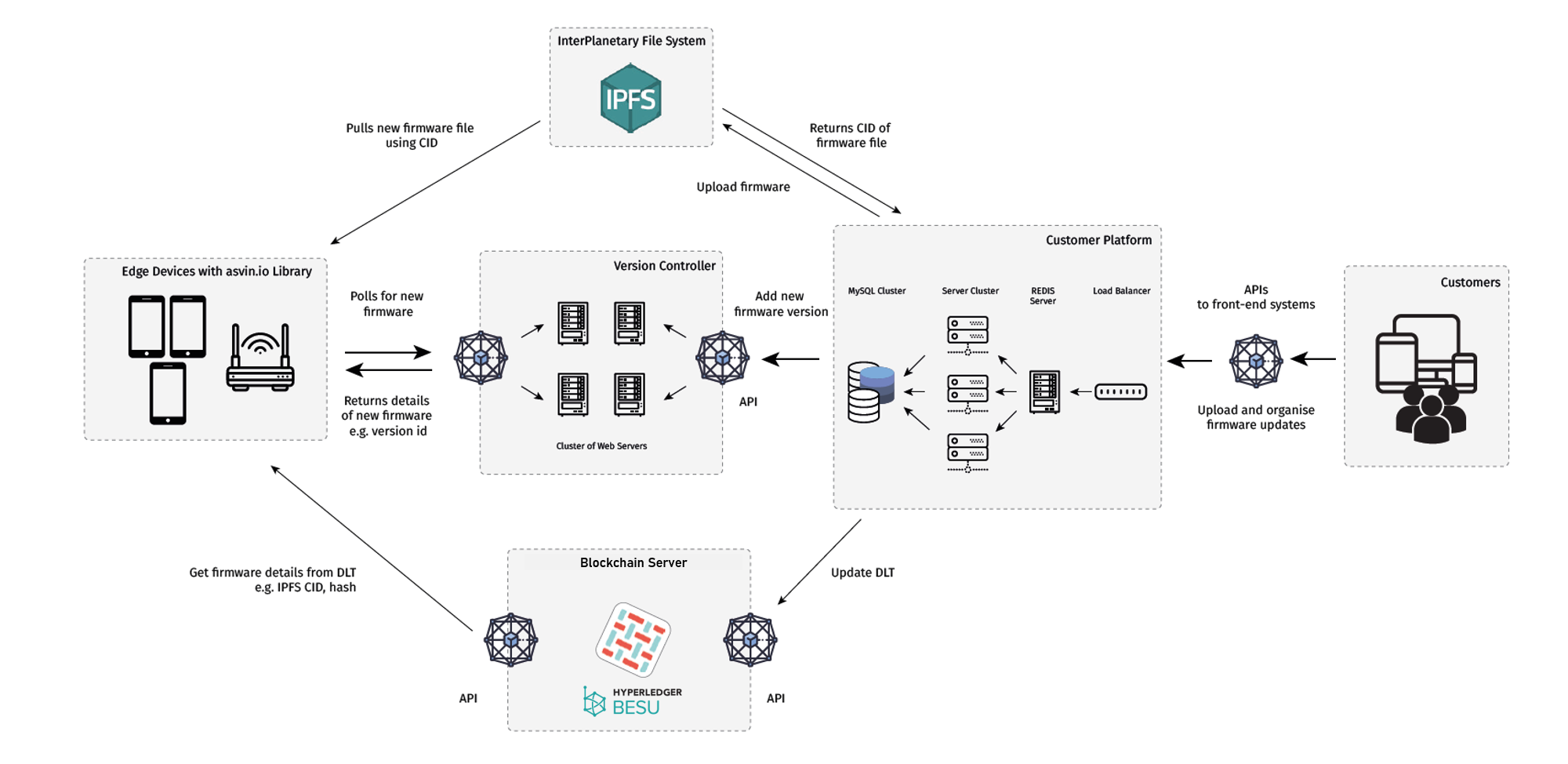
Asvin Model¶
In this section we will take a brief look at asvin’s architecture and briefly explain its components. Some relevant concepts and keywords are also mentioned below.
Customer Platform¶
asvin provides a user-friendly customer platform to abstract the complexities of the background processes to register devices, setup & schedule firmware rollouts, define group actions on registered devices, and to blacklist devices. The customer platform also displays information related to firmware updates and provides the current version of edge devices.
Version controller¶
The version controller maintains updated information of firmware avaliable for a particular edge device or device group on the asvin.io platform. It is one of the core components of the asvin architecture.
Interplanetary FileSystem¶
Interplanetary FileSystem or IPFS is a distributed peer-to-peer hypermedia protocol designed for storing and sharing data in a distributed file system. IPFS serves as one of the core components of the asvin architecture. asvin uses IPFS protocol to store firmware, updates and security patches. Check out the detailed notes on IPFS here.
Content Identifier
Data exchanges on decentralised platforms like IPFS depends upon content-based addressing rather than local addressing to securely locate and identify data. A Content Identifier (CID) is a self-describing content address identifier which is a cryptographic hash, typically SHA-256, which is 32 bytes. The CID for a binary image file stored on an IPFS network might be QmcRD4wkPPi6dig81r5sLdrtd1gDCL4zgpEj9CfuRrGbzF.
Blockchain¶
The asvin platform uses blockchain technology to store all of the transactions executed on the asvin.io network including: device registration, firmware upload, device update, firmware update, user registration, etc. All these transactions are connected with hashes and stored in blocks which are again linked to a secured hash. For the asvin platform we use the Hyperledger Fabric and Hyperledger besu blockchains.
Distributed Ledger
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is a digital system for recording the transaction of assets in which the details of specific transactions are recorded in multiple places. Unlike traditional databases, distributed ledgers have no central data storage or administration functionality. The above mentioned blockchain is a type of DLT.
Smart Contracts
A smart contract is a computer program or a digital transaction protocol which is intended to automatically execute, control or document legally relevant events and actions according to the terms of a contract or an agreement. The objective of a smart contract is to reduce the need of trusted intermediators, arbitration, enforcement costs, fraud losses, as well as the risk mitigation of malicious attacks and accidental exceptions.
Edge Devices¶
Edge devices are end-points in the asvin.io architecture and in an IoT network which control, manage and solve a specific physical task: For instance, edge devices turn on a smart washing machine in a house, monitoring temperature and humidity in a chemical plant or an air quality sensor installed in a city. These devices have microcontrollers and sensors at their core and with their small footprints these edge devices are easy to manage in remote areas under extreme environmental conditions. Examples of edge devices in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) include process monitoring sensors, smart meters, Lora nodes, smoke detectors, etc.